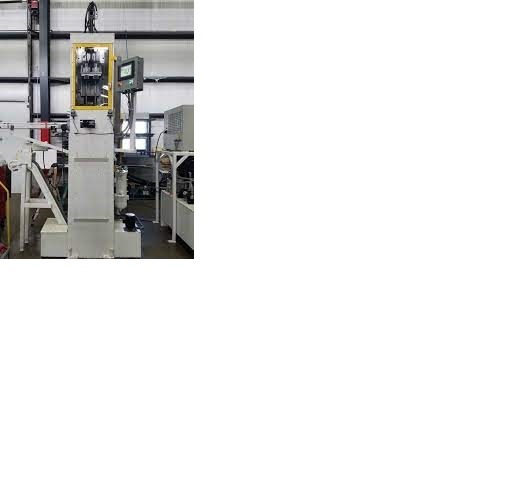
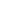
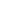
Broaching Machine
Product Details:
Broaching Machine Price And Quantity
- 1 Piece
- 1200000.00 - 1600000.00 INR/Piece
- 1400000 INR/Piece
Product Description
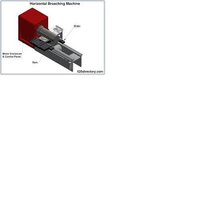
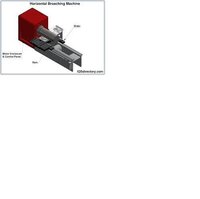
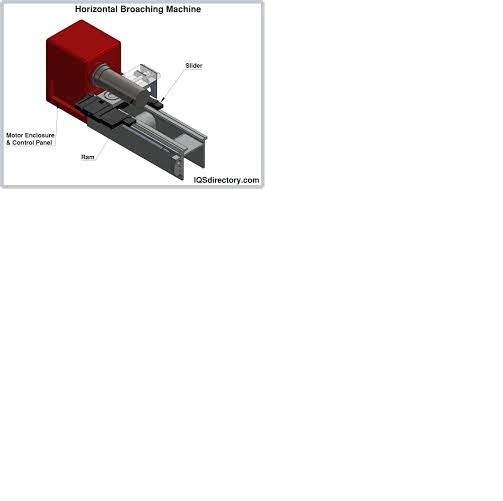
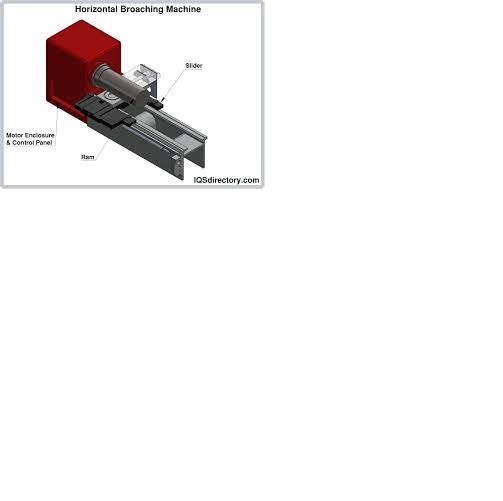
Broaching is a machining process that uses a toothed tool, called a broach, to remove material. There are two main types of broaching: linear and rotary. In linear broaching, which is the more common process, the broach is run linearly against a surface of the workpiece to produce the cut. Linear broaches are used in a broaching machine, which is also sometimes shortened to broach. In rotary broaching, the broach is rotated and pressed into the workpiece to cut an axisymmetric shape. A rotary broach is used in a lathe or screw machine. In both processes the cut is performed in one pass of the broach, which makes it very efficient.
Broaching is used when precision machining is required, especially for odd shapes. Commonly machined surfaces include circular and non-circular holes, splines, keyways, and flat surfaces. Typical workpieces include small to medium-sized castings, forgings, screw machine parts, and stampings. Even though broaches can be expensive, broaching is usually favored over other processes when used for high-quantity production runs.
 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese